Did you ever want to fly a plane yourself, but lacked the money or ability to do so? Are you a real pilot looking to improve your skills without having to take off? Do you want to try some dangerous maneuvers without risking your life? Or do you just want to have fun with a more serious game without any violence? If any of these questions apply to you, PC flight simulators are just for you.
You may already have some experience using Microsoft’s © Flight Simulator or any other of the commercially available PC flight simulators. As the price tag of those is usually within the $50 range, buying one of them should not be a serious problem given that running any serious PC flight simulator requires PC hardware within the $1500 range, despite dropping prices.
With so many commercially available flight simulators, why would we spend thousands of hours of programming and design work to build a free flight simulator? Well, there are many reasons, but here are the major ones:
The points mentioned above form the basis of why we created FlightGear. With those motivations in mind, we have set out to create a high-quality flight simulator that aims to be a civilian, multi-platform, open, user-supported, and user-extensible platform. Let us take a closer look at each of these characteristics:
At present, there is no known flight simulator - commercial or free - supporting such a broad range of platforms.
The GPL is often misunderstood. In simple terms it states that you can copy and freely distribute the program(s) so licensed. You can modify them if you like and even charge as much money as want to for the distribution of the modified or original program. However, you must freely provide the entire source code to anyone who wants it, and it must retain the original copyrights. In short:
The full text of the GPL can be obtained from the FlightGear source code or from
Without doubt, the success of the Linux project, initiated by Linus Torvalds, inspired several of the developers. Not only has Linux shown that distributed development of highly sophisticated software projects over the Internet is possible, it has also proven that such an effort can surpass the level of quality of competing commercial products.

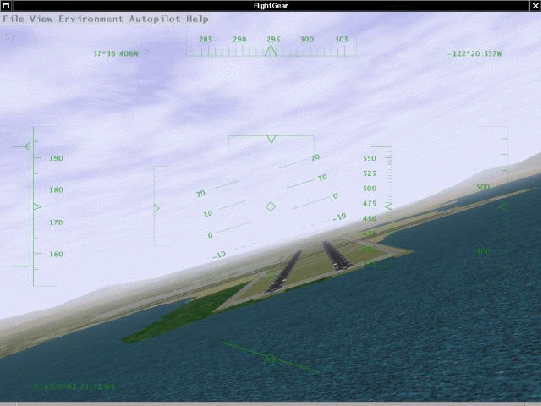
Fig. 1: FlightGear under UNIX: Bad approach to San Francisco International - by one of the authors of this manual. . .
In comparison to other recent flight simulators, the system requirements for FlightGear are not extravagant. A decent PIII/800, or something in that range, should be sufficient given you have a proper 3-D graphics card. Additionally, any modern UNIX-type workstation with a 3-D graphics card will handle FlightGear as well.
One important prerequisite for running FlightGear is a graphics card whose driver supports OpenGL. If you don’t know what OpenGL is, the overview given at the OpenGL website
says it best: “Since its introduction in 1992, OpenGL has become the industry’s most widely used and supported 2-D and 3-D graphics application programming interface (API)...”.
FlightGear does not run (and will never run) on a graphics board which only supports Direct3D. Contrary to OpenGL, Direct3D is a proprietary interface, being restricted to the Windows operating system.
You may be able to run FlightGear on a computer that features a 3-D video card not supporting hardware accelerated OpenGL - and even on systems without 3-D graphics hardware at all. However, the absence of hardware accelerated OpenGL support can bring even the fastest machine to its knees. The typical signal for missing hardware acceleration are frame rates below 1 frame per second.
Any modern 3-D graphics featuring OpenGL support will do. For Windows video card drivers that support OpenGL, visit the home page of your video card manufacturer. You should note that sometimes OpenGL drivers are provided by the manufacturers of the graphics chip instead of by the makers of the board. If you are going to buy a graphics card for running FlightGear, one based on a NVIDIA chip (TNT X/Geforce X) might be a good choice.
To install the executable and basic scenery, you will need around 50 MB of free disk space. In case you want/have to to compile the program yourself you will need about an additional 500 MB for the source code and for temporary files created during compilation. This does not include the development environment, which will vary in size depending on the operating system and environment being used. Windows users can expect to need approximately 300 MB of additional disk space for the development environment. Linux and other UNIX machines should have most of the development tools already installed, so there is likely to be little additional space needed on those platforms.
For the sound effects, any capable sound card should suffice. Due to its flexible design, FlightGear supports a wide range of joysticks and yokes as well as rudder pedals under Linux and Windows. FlightGear can also provide interfaces to full-motion flight chairs.
FlightGear is being developed primarily under Linux, a free UNIX clone (together with lots of GNU utilities) developed cooperatively over the Internet in much the same spirit as FlightGear itself. FlightGear also runs and is partly developed under several flavors of Windows. Building FlightGear is also possible on a Macintosh OSX and several different UNIX/X11 workstations. Given you have a proper compiler installed, FlightGear can be built under all of these platforms. The primary compiler for all platforms is the free GNU C++ compiler (the Cygnus Cygwin compiler under Win32).
If you want to run FlightGear under Mac OSX we suggest a Power PC G3 300 MHz or better. As a graphics card we would suggest an ATI Rage 128 based card as a minimum. Joysticks are supported under Mac OS 9.x only; there is no joystick support under Max OSX at this time.
Concerning the FlightGear source code there exist two branches, a stable branch and a developmental branch. Even version numbers like 0.6, 0.8, and (someday hopefully) 1.0 refer to stable releases, while odd numbers like 0.7, 0.9, and so on refer to developmental releases. The policy is to only do bug fixes in the even versions, while new features are generally added to odd-numbered versions which, after all things have stabilized, will become the next stable release with a version number calculated by adding 0.1.
To add to the confusion, there usually are several versions of the ”unstable” branch. First, there is a ”latest official release” which the pre-compiled binaries are based on. It is available from
ftp://ftp.flightgear.org/pub/fgfs/Source/FlightGear-X.Y.Z.tar.gz
For developers there exist CVS snapshots of the source code, available from
ftp://www.flightgear.org/pub/flightgear/Devel/Snapshots/.
While theses are quite recent, they may still be sometimes a few days back behind development. Thus, if you really want to get the very latest and greatest (and, at times, buggiest) code, you can use a tool called anonymous cvs available from
to get the recent code. A detailed description of how to set this up for FlightGear can be found at
http://www.flightgear.org/cvsResources/.
Unfortunately, the system implemented above does not really work as it should. As a matter of fact, the stable version is usually so much outdated, that it does not at all reflect the state of development FlightGear has reached. Given that the recent developmental versions on the other hands may contain bugs (. . . undocumented features), we recommend using the ”latest official (unstable) release” for the average user. This is the latest version named at
http://www.flightgear.org/News/;
usually this is also the version which the binary distributions available at
http://www.flightgear.org/Downloads/
are based on. If not otherwise stated, all procedures in this “Installation and Getting Started” will be based on these packages.
Historically, FlightGear has been based on a flight model it inherited (together with the Navion airplane) from LaRCsim. As this had several limitations (most important, many characteristics were hard wired in contrast to using configuration files), there were several attempts to develop or include alternative flight models. As a result, FlightGear supports several different flight models, to be chosen from at runtime.
The most important one is the JSB flight model developed by Jon Berndt. Actually, the JSB flight model is part of a stand-alone project called JSBSim, having its home at
http://jsbsim.sourceforge.net/.
Concerning airplanes, the JSB flight model at present provides support for a Cessna 172, a Cessna 182, a Cessna 310, and for an experimental plane called X15. Jon and his group are gearing towards a very accurate flight model, and the JSB model has become FlightGear’s default flight model.
As an interesting alternative, Christian Mayer developed a flight model of a hot air balloon. Moreover, Curt Olson integrated a special ”UFO” slew mode, which helps you to quickly fly from point A to point B.
Recently, Andrew Ross contributed another flight model called YASim for Yet Another Simulator. At present, it sports another Cessna 172, a Turbo 310, a fairly good DC-3 model, along with a Boeing 747, Harrier, and A4. YASim takes a fundamentally different approach since it’s based on geometry information rather than aerodynamic coefficients. Where JSBSim will be exact for every situation that is known and flight tested, but may have odd and/or unrealistic behavior outside normal flight, YASim will be sensible and consistent in almost every flight situation, but is likely to differ in performance numbers.
As a further alternative, there is the UIUC flight model, developed by a team at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. This work was initially geared toward modeling aircraft in icing conditions together with a smart icing system to better enable pilots to fly safely in an icing encounter. While this research continues, the project has expanded to include modeling ”nonlinear” aerodynamics, which result in more realism in extreme attitudes, such as stall and high angle of attack flight. Two good examples that illustrate this capability are the Airwave Xtreme 150 hang glider and the 1903 Wright Flyer. For the hang glider, throttle can be use to fly to gliding altitude or Ctrl-U can be used to jump up in 1000-ft increments. Try your hand at the unstable Wright Flyer and don’t stall the canard! Considerable up elevator trim will be required for level flight. In general, the aerodynamics are probably very close to the original Wright Flyer as they are partly based on experimental data taken on a replica tested recently at the NASA Ames Research Center. Also included are two more models, a Beech 99 and Marchetti S-211 jet trainer, which are older generation UIUC/FGFS models and based on simpler ”linear” aerodynamics. More details of the UIUC flight model and a list of aircraft soon to be upgraded can be found on their website at
http://amber.aae.uiuc.edu/ m-selig/apasim.html
m-selig/apasim.html
Note that the 3D models of the UIUC airplanes can be downloaded from a site maintained by Wolfram Kuss
http://home.t-online.de/home/Wolfram.Kuss/
It is even possible to drive FlightGear’s scene display using an external FDM running on a different computer - although this might not be a setup recommended to people just getting in touch with FlightGear.
There is little, if any, material in this Guide that is presented here exclusively. You could even say with Montaigne that we ”merely gathered here a big bunch of other men’s flowers, having furnished nothing of my own but the strip to hold them together”. Most (but fortunately not all) of the information herein can also be obtained from the FlightGear web site located at
Please, keep in mind that there are several mirrors of the FlightGear web sites, all of which are linked to from the FlightGear homepage listed above. You may prefer to download FlightGear from a mirror closer to you than from the main site.
This FlightGear Installation and Getting Started manual is intended to be a first step towards a complete FlightGear documentation. The target audience is the end-user who is not interested in the internal workings of OpenGL or in building his or her own scenery. It is our hope, that someday there will be an accompanying FlightGear Programmer’s Guide (which could be based on some of the documentation found at
http://www.flightgear.org/Docs;
a FlightGear Scenery Design Guide, describing the Scenery tools now packaged as TerraGear; and a FlightGear Flight School package.
As a supplement, we recommend reading the FlightGear FAQ to be found at
http://www.flightgear.org/Docs/FlightGear-FAQ.html
which has a lot of supplementary information that may not be included in this manual.
We kindly ask you to help us refine this document by submitting corrections, improvements, and suggestions. All users is invited to contribute descriptions of alternative setups (graphics cards, operating systems etc.). We will be more than happy to include those into future versions of this Installation and Getting Started (of course not without giving credit to the authors).
While we intend to continuously update this document, we may not be able to produce a new version for every single release of FlightGear. To do so would require more manpower that we have now, so please feel free to jump in and help out. We hope to produce documentation that measures up to the quality of FlightGear itself.